Last month at Microsoft Connect 2017, Azure Cosmos DB received several new updates including support for using the Cassandra NoSQL database API and increased guarantees for availability. With the Cassandra NoSQL database API, customers can run operations inside Cosmos DB on a data model. The availability guarantee moves from 99.99 percent to 99.999 percent.
Ike Ellis, a Microsoft MVP and a partner at the independent development house Crafting Bytes in San Diego, California, said:
Now in preview, Microsoft's Cassandra API works with Azure Cosmos DB. This is a Swiss army knife-style database -- sometimes described as a multimodel database -- that the company spawned earlier this year from an offering known as DocumentDB. The Cassandra update fills in an important part of the Azure cloud database picture.
Microsoft Cosmos DB is a managed database service available in all data centers around the world. The database service supports several data models like graph, column-family, key-value and document. With support for Cassandra, customers can now lift and shift their on-premise Cassandra enabled application into the Cosmos DB to leverage all the benefits the service offers. Customers do not need to manage a Cassandra cluster anymore or modifying the configuration. Moreover, Microsoft guarantees with its SLAs four nines towards throughput regardless of the volume of stored data and five nines for availability.
Scott Guthrie, executive vice president of the Cloud and Enterprise group at Microsoft, said during Connect 2017:
Cassandra is an open-source distributed database management system that can be deployed on commodity servers. The new API will allow developers to reuse their existing code and use the globally-distributed Cosmos DB NoSQL service as the basis for "Cassandra-as-a-service" implementations.
Before provisioning an instance of Cosmos DB customers can select the new Cassandra API. Once provisioned a Cassandra application can be connected to the Cosmos DB instance using a simple connection code snippet. In the Cosmos DB instance, a developer can use the CQL shell to create a Cassandra key-space in a table using CQL statements. The commands are executed against a Cosmos DB endpoint, unaware of that it is communicating with the Cosmos DB instance.

Source: (screenshot) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Sf4McGN1AQ&feature=youtu.be
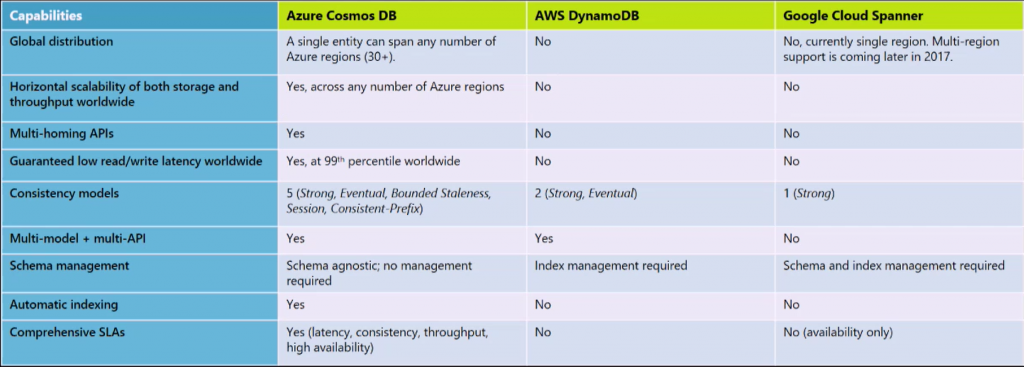
The public cloud providers Google, Microsoft and Amazon each have database services available in the cloud. Earlier this year Microsoft released a comparison chart of database services of each cloud provider: Cosmos DB, AWS Dynamo DB, and Google Cloud Spanner. In the comparison chart, Cosmos stands out with its multi-model and multi-API support, global distribution, consistency models, central management and SLA’s.
However, during AWS re:Invent, Amazon announced several updates to Dynamo DB like global tables and on-demand backup, and it has over a hundred thousand customers. Moreover, Amazon customers have migrated from Cassandra to Dynamo DB. Hence, Microsoft’s Cosmos DB is not the only option for customers looking for a database service in the cloud for their Cassandra applications.

Source: (screenshot) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EFDDjzIGxA0
In response to development with Cosmos DB and AWS Dynamo DB, Google has enhanced its database service Cloud spanner. It now offers five nines availability with no downtime, transactions and synchronous replication extend across multiple regions and continents, and supporting a more extensive range of application workloads. The only differentiator left between Cosmos DB and its competing services, AWS Dynamo DB, and Google Cloud Spanner, is the multi-model and multi-API support. Specifically, customers looking for flexibility in the models and API support could choose Cosmos DB.
Christoph Leinemann, senior director, data engineering, at Jet.com on their adoption of Cassandra in Cosmos DB on the Azure blog said:
We are using the Cassandra API on Azure Cosmos DB for several mission-critical use cases. In particular, the geo-redundancy and dynamic scale of the solution are key advantages, and we look forward to reaping more benefits in the future.